Industry Transformation Map (ITM)

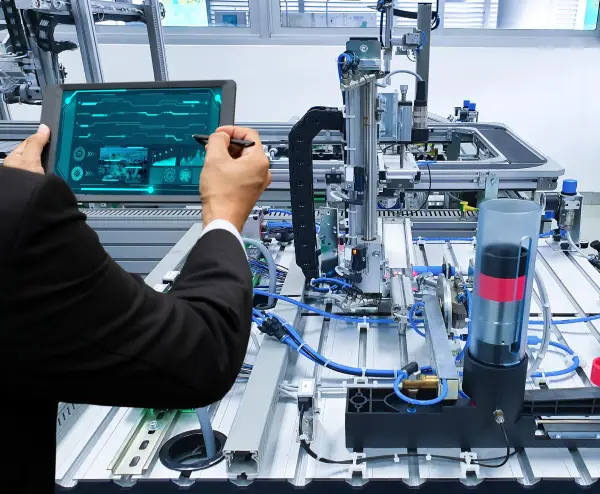
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
DFMA is an engineering methodology that focuses on reducing time-to-market and total production costs by prioritizing both the ease of manufacture for the product’s parts and the simplified assembly of those parts into the final product – all during the early design phases of the product lifecycle.
DFMA represents a harmonious combination of Design for Manufacturing (DFM) and Design for Assembly (DFA).
DFM is concerned with selecting cost-effective raw materials and attempting to minimize the complexity of manufacturing operations during the product design phase in order to reduce the overall manufacturing time and costs for product components.
Design for Manufacturing
(DFM)
Design for Manufacturing
(DFM)
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly
(DFMA)
(DFMA)
DFM is concerned with selecting cost-effective raw materials and attempting to minimize the complexity of manufacturing operations during the product design phase in order to reduce the overall manufacturing time and costs for product components.
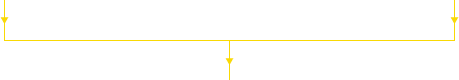
Steps for applying DFMA during product design
- DFA analysis leading to simplification of the product structure.
- Early cost estimation of parts for both the original design and the modified design.
- Selecting the best material and process to be used.
- Conduct a thorough DFM analysis after finalizing the material and process selections.

Flow diagram shows various steps undertaken in a DFMA study
Design Concept


Design for assembly (DFA)
Suggestions for simplification of
product structure
product structure
Selection of materials and process
and early cost estimation
and early cost estimation
Suggestions for more economic
materials and processes
materials and processes
Best design concept
Design for manufacturing (DFM)
Detailed design for minimum
manufacturing costs
manufacturing costs
Prototype
Production
the invite over slack


Today’s problem with
product design
- Tends to become more complex.
- Made or required in an increasingly large number.
- Intended to satisfy a wide variation in user population.
- Required to compete aggressively with similar products.
- Required to consistently high quality
Advantages of applying
DFMA during product design
- DFMA not only reduces the manufacturing cost of the product but also helps reduce the time to market and the quality of the product.
- From the point of view of assembly and manufacture, DFMA provides a systematic procedure for analyzing a proposed design.
- Any reduction in the number of parts reduces the cost as well as the inventory.
- DFMA tools encouraged dialogue between the designer and manufacturing engineer during the early stages of design.


Why DFMA is not being
implemented widely?
01. No Time
Designers are constrained to minimize their “design to manufacture time” for a new product.
02. Not Invented Here
Very often designers provide enough resistance to adopting new techniques.
03. The Ugly Baby Syndrome
Designer ego crashes if there is some suggestion for design change.


04. Low Assembly Cost
Since the assembly cost of a particular product is less as compared to the total material and manufacturing cost, DFA analysis is not required.
05. Low Volume
Often it is expressed that DFMA is applicable for large quantity production.





Advanced Manufacturing and Assembly (AMA)
- AMA involves creating a factory-like setting to automate fabrication that improves productivity, quality, and the work environment.
- AMA promotes manpower-efficient technologies in the construction process, reducing firms’ reliance on low-skilled foreign manpower and raising productivity.
- In Singapore, BCA has included AMA as one of the key transformation areas in the new Building Environment Industry Transformation Map (ITM).
- Moving forward, BCA targets increasing the DFMA adoption rate by GFA from 44% today to 70% by 2025.
- Under AMA, more off-site production will be done in a factory environment with greater adoption of automation. By improving the quality of work and working environments, including at the construction site, the industry hopes to attract and retain talent in the sector.
- The shift from a project-based building approach to a modular, product-based one also enables industry firms to reap greater economies of scale.


