Industry Transformation Map (ITM)

Built Environment ITM
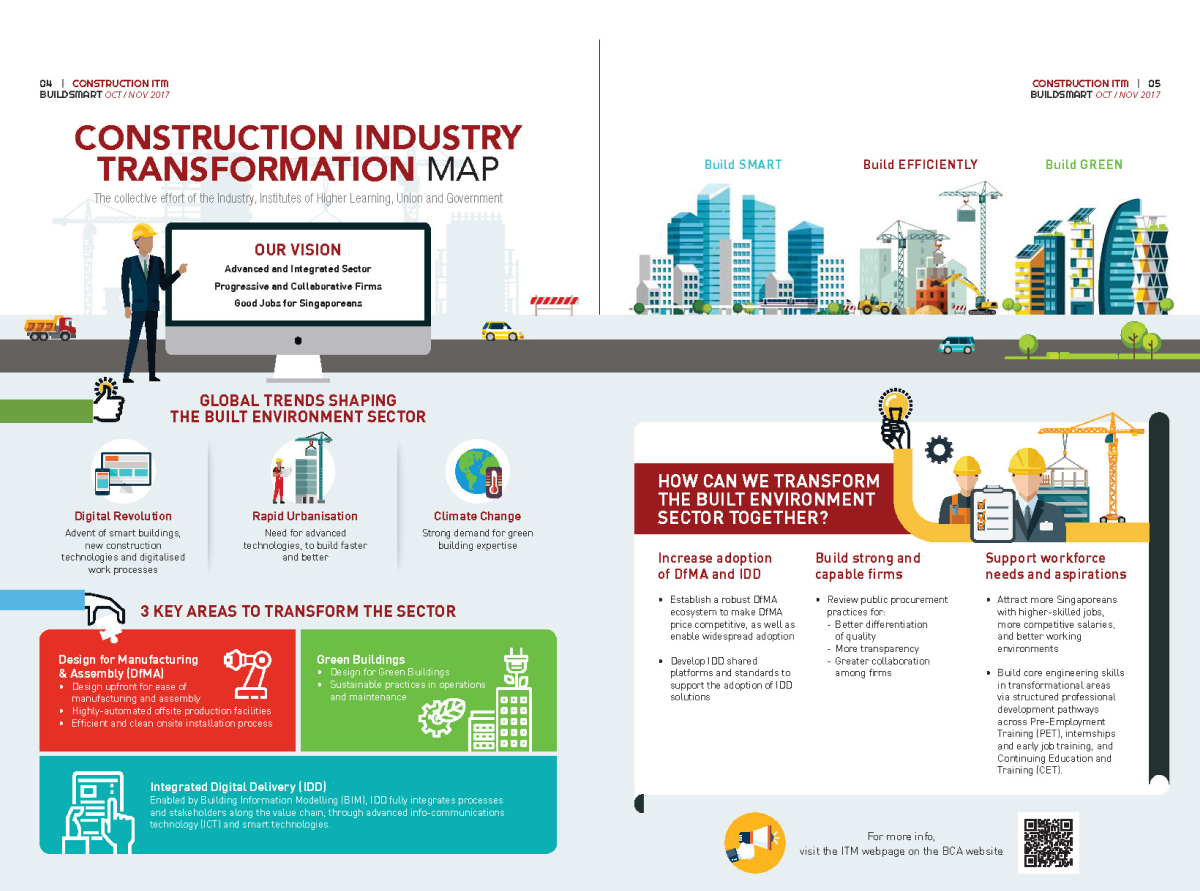
Building a World-class And Resilient Sector
Comprising global champions and value chain alliances, offering innovative, sustainable, & in demand solutions, and quality
jobs, supported by a competent Singapore core.
jobs, supported by a competent Singapore core.
-
Integrated Planning and Design
- Drive collaboration across value chain to enable better planning from the onset, and optimise building design for downstream construction and maintenance.
- Create a conducive environment for collaboration and regulatory submissions through common data standards, with a data-rich Building Information Modeling model that is used across the project lifecycle.
-

-

-
Advanced Manufacturing and Assembly
- Automate fabrication in factories to improve productivity, quality and work environment.
- Drive co-location of synergistic construction activities (e.g. aggregate storage, batching plants, precast plants) to optimise land use and streamline logistical processes.
-
 Sustainable Urban Systems
Sustainable Urban Systems
- Accelerate our decarbonisation efforts to support our net zero aspirations, and create a more sustainable and liveable built environment.
- Streamline operations and improve maintenance of buildings enabled by Integrated, Aggregated and Smart Facilities Management.
-

KEY ENABLERS
Drive value chain
transformation
Spur innovation and technology
to build capable firms
Groom a competent workforce
with fulfilling careers
Strengthen resilience against
future disruptions
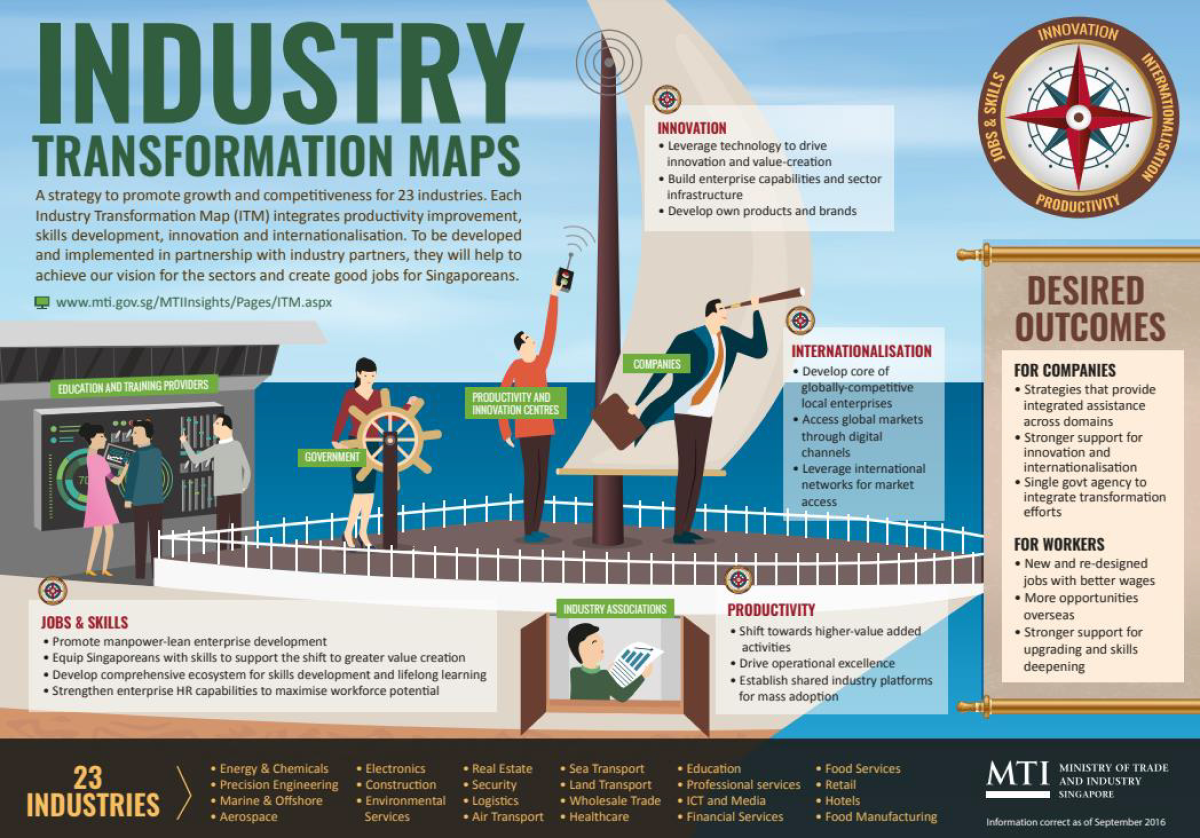
What are Industry Transformation Maps (ITM)?
Industry transformation maps are frameworks designed by the Future Economy Council (FEC) to encourage collaboration among stakeholders from different industries and to enable companies to understand the developing business environment. ITMs bring together government, trade associations and chambers, private companies, economic agencies, and other stakeholders from 23 industries to address sector issues.

Four categories describe the framework's
transformation strategies are:

- Developing human capital
This vision involves providing grants for internships to strengthen the country’s pool of leaders and build talents for different industries. It also encourages employer-led capacity building and other training sessions to equip you with skills and knowledge on emerging business trends.
- Promoting collaboration and strong networks
The FEC seeks to establish and encourage partnerships within industries and across various sectors. Through collaboration, stakeholders can appreciate how different sectors are interdependent and identify ways to address issues within each industry jointly.
- Building enterprise capabilities
The focus is on connecting businesses with telecommunication providers, Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) and banks to promote technology adoption. It also encompasses the Scale-up SG programme, where public and private sector partners select a few small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and nurture them to become future industry leaders.
- Enhancing enterprise ecosystems
This strategy seeks to make the compliance landscape and regulatory requirements more business-friendly. FEC works with industry stakeholders and the government to review existing business laws to make them more favourable for SMEs to thrive.


Who oversees ITMs?
The FEC oversees the designing and implementation of the ITMs. It has seven clusters comprising political officeholders and stakeholders from the private sector to help it create and deploy the transformation frameworks. These clusters are interdependent but have areas of specialisation:
- Connectivity cluster
- Advanced manufacturing and trade (AMT) cluster
- Urban systems cluster
- Human health and potential (HHP) cluster
- Modern services cluster
- Resources and environmental stability cluster
- Lifestyle cluster
ITM Industries
The Future Economy Council works with the government and stakeholders to implement the $4.5 billion ITMs programme. The primary aim is to create good jobs and ample business opportunities across all sectors. FEC has six sub-committees to help achieve this mandate:
Manufacturing
Precision engineering, Energy and chemicals, Marine and offshore, Aerospace, Electronics
Trade and
connectivity
Air transport, Logistics, Land transport, Sea transport, and Wholesale trade
Built Environment
Construction, Real estate, Security, and Environmental Services
Modern services
Professional services, financial services, ICT and media
Essential domestic
service
Healthcare, Education
Lifestyle
Food and manufacturing, Food services, Hotel, Retail